
会社概要About us
EneCoat Technologies will exhibit at INPEX CORPORATION booth at ADIPEC 2025 in Abu Dhabi
We are pleased to announce that we will exhibit our developed “Perovskite Solar Cell Module” at INPEX CORPORATION booth during ADIPEC 2025, held in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, for four days from Monday, November 3 to Thursday, November 6, 2025.
ADIPEC is the world’s largest event in the energy sector, attracting over 200,000 attendees annually. It features the latest business and technology shaping the future of energy, with participation from over 2,200 companies and organizations spanning the global energy industry, including ADNOC (UAE). We invite you to visit our booth during the exhibition period.
ADIPEC Exhibition & Conference | November 3-6, 2025
Please note that advance registration is required to attend this exhibition. For details, please check the official ADIPEC Exhibition website.
■Exhibition Overview
Dates: Monday, November 3 to Thursday, November 6, 2025, 10:00 AM to 6:30 PM (Closes at 5:30 PM on the final day only)
Venue: ADNEC Centre in Abu Dhabi (Al Khaleej Al Arabi St – Al Rawdah – Al Ma’arid – Abu Dhabi)
HP: adipec.com
Exhibition Location: Hall6 – 6230

Selected for Final Phase of NEDO Green Innovation Fund
Accelerating Mass Production Technology Development for Film-Type Perovskite Solar Cells, Paving the Way for Full-Scale Entry into Outdoor Installation Applications
EneCoat Technologies Co., Ltd. (Head office: Kumiyama-cho, Kuse-gun, Kyoto Prefecture; CEO: Naoya Kato; hereinafter referred to as “EneCoat”) is pleased to announce that a project “Mass production technology development and demonstration project for the social implementation of perovskite solar cells with high installation flexibility” (hereinafter referred to as “this project”) for the “Green Innovation Fund Project/Project for Demonstration of Next-generation Solar Cells” was adopted on 10 September 2025. This project was publicly solicited by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (hereinafter referred to as “NEDO”).
This project is the final phase of the “Research and Development and Social Implementation Plan for Project for development of next-generation solar cells” formulated by the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) , and aims to reduce power generation costs under certain conditions (solar radiation conditions, etc.) to 14 yen/kWh or less by fiscal year 2030. Following on from the current phase (Project for practical realization of next-generation solar cells, adopted on December 28, 2021), EneCoat will be working on research and development and social implementation of next-generation solar cells (perovskite solar cells) as one of the major players in Japan, with the support of the Green Innovation Fund.
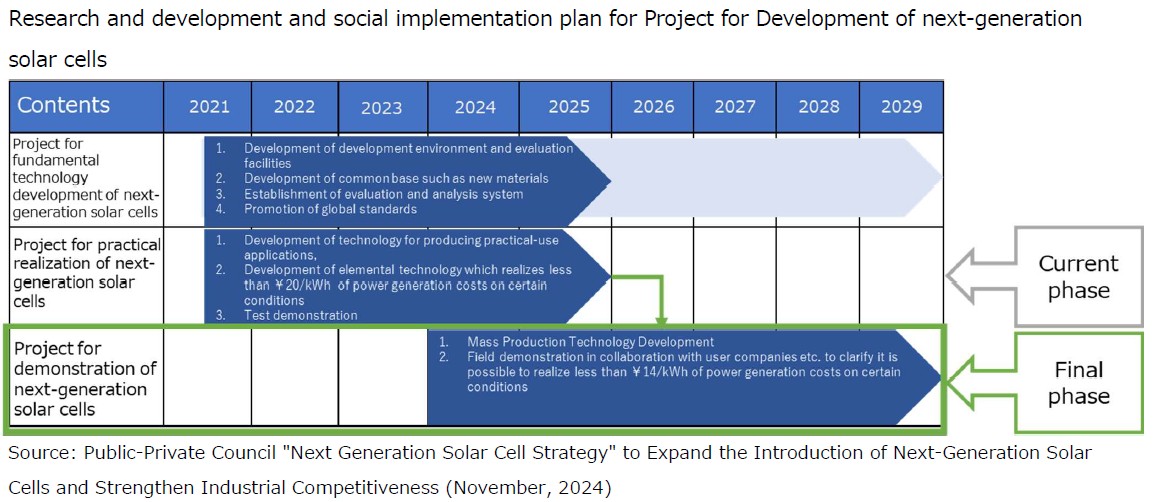
EneCoat also aims to leverage this project as an opportunity to fully enter the huge market for Selected for Final Phase of NEDO Green Innovation Fund Accelerating Mass Production Technology Development for Film-Type Perovskite Solar Cells, Paving the Way for Full-Scale Entry into Outdoor Installation Applications outdoor stationary applications with perovskite solar cells. Kyoto University, where EneCoat is originated, will participate as an outsourced entity in this project, and a powerful corporate-academia alliance (hereinafter referred to as the “Consortium”) will be formed with the following institutions.
EneCoat will be fully prepared to steadily translate the results of its research and development into social implementation toward achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, and then promote large-scale dissemination both domestically and internationally. Furthermore, the implementation of this project will see the full-scale introduction of the “roll-to-roll method” as a production method for the first time since the company’s establishment, and will strongly promote the creation of a market for the “filmtype” method, EneCoat’s specialty.

The global race to develop perovskite solar panels has already entered the large-scale production phase, with Chinese companies taking on conventional crystalline silicon solar panels with their “glasstype” solar panels. Meanwhile, in Japan, there are hopes that a market will be formed soon by taking advantage of the light, thin, and flexible (bendable) characteristics of film-type perovskite solar panels, and introducing them into places where crystalline silicon solar panels cannot be installed (such as roofs and building walls with low load-bearing capacity), and this project will target this market.
The Japanese government’s “Seventh Strategic Energy Plan,” approved by the Cabinet in February 2025, and the “Next Generation Solar Cell Strategy,” revealed by METI at the end of November 2024, set out a clear numerical target of “aiming to introduce a cumulative total of approximately 20 GW of perovskite solar cells by 2040.” In response to this, competition to build large-scale production systems is expected to intensify in Japan as well, and EneCoat has formed the above consortium to enter this competition and will lead research and development as a core member of the consortium.
【Contact for inquiries regarding this matter】
E-mail:info@enecoat.com
EneCoat Technologies has been selected for the 2025 Forbes Asia 100 to Watch list.
EneCoat Technologies has been selected for this year’s Forbes Asia 100 to Watch list.
This fifth edition of the Forbes Asia 100 to Watch list features 100 fast-growing small companies and startups in the Asia-Pacific region are driving innovation across 10 sectors including biotechnology, space technology, retail, and finance.
Learn more here http://www.forbes.com/100towatch
Achieved a conversion efficiency of over 30% with a perovskite/silicon 4-terminal tandem solar cell.
EneCoat Technologies Co., Ltd (Head Office: Kumiyama-cho, Kuze-gun, Kyoto; President: Naoya Kato) has achieved a conversion efficiency of over 30% with a 4-terminal tandem cell consisting of stacked perovskite and crystalline silicon solar cells in a joint development project with Toyota Motor Corporation. Ltd.
This achievement underscores the profound research and development capabilities of both companies in the field of perovskite solar cells and accelerates the practical application of high-efficiency solar cells, which is the objective of the joint development project.
Solar cells used in automobiles, satellites, and other applications are required to have the highest possible conversion efficiency due to the limited area available for their installation. While the theoretical conversion efficiency of perovskite solar cells alone is 33.7%, the theoretical conversion efficiency of tandem-type solar cells, which are made by stacking perovskite solar cells and crystalline silicon solar cells, is 43.8%, far exceeding the value of standalone solar cells.
Tandem solar cells have a structure with a perovskite solar cell and a crystalline silicon solar cell, each of which has its own power generation layer, in order from the light-receiving side. The perovskite solar cell first generates power with light energy in the visible light region, and the crystalline silicon solar cell generates power with light energy in the infrared region, which is not absorbed by the perovskite. The perovskite solar cell is the first to generate electricity. Therefore, perovskite solar cells are required to have both high power generation capability in visible light and the ability to transmit infrared light to crystalline silicon without loss. This time, the two companies focused on the transmittance of perovskite solar cells and succeeded in improving the infrared transmittance to 81%.
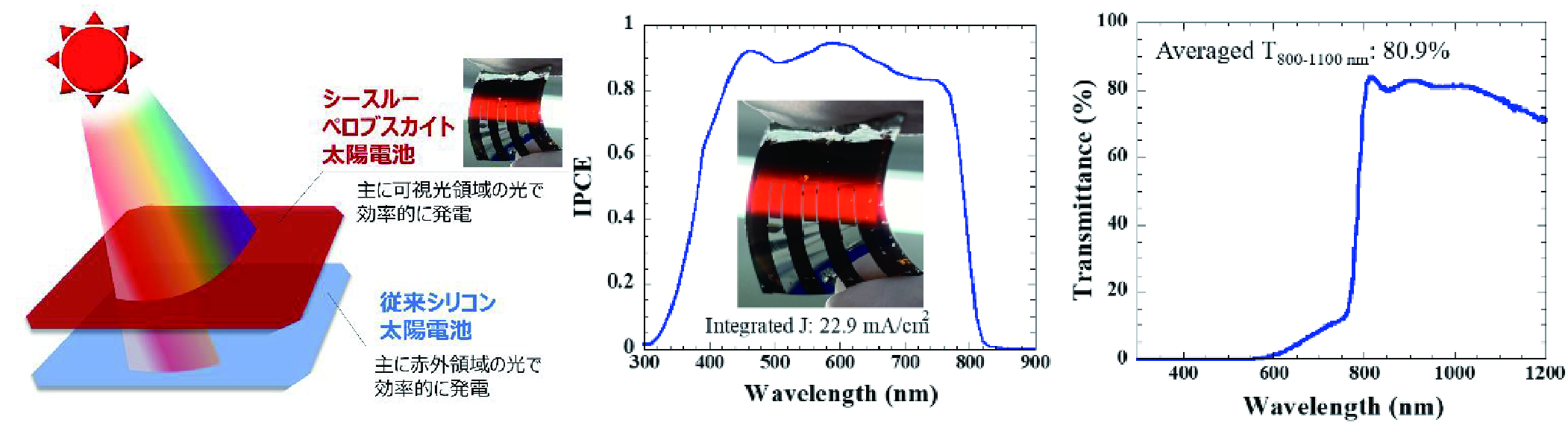
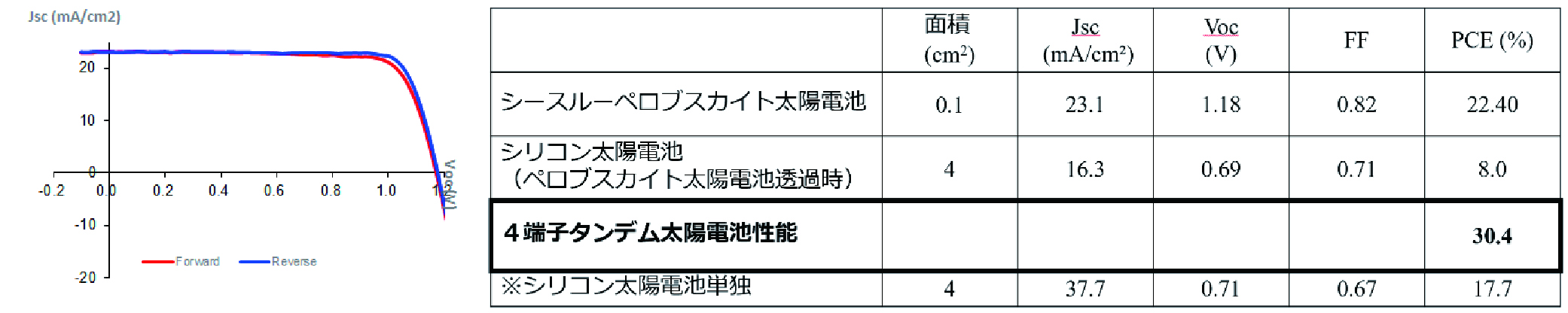
When solar cells are installed on the roof of an automobile, they are required to follow the roof shape. The two companies developed a film-type perovskite solar cell and achieved a conversion efficiency of 22.4%, which is extremely high for a see-through type solar cell. 22.4% conversion efficiency and 81% infrared transmittance have never been reported before in the world, proving the superior technology of the two companies. By combining this film-type perovskite solar cell with a crystalline silicon solar cell, we have achieved a world-class conversion efficiency of 30.4% as a 4-terminal tandem solar cell.
The conversion efficiency values obtained in this development were measured in a small area at the cell level, and we will continue to develop the large size modules of solar cells to achieve the practical application of high efficiency solar cells that will bring benefits to users.
The results will be presented at The Asia-Pacific International Conference on Perovskite, Organic Photovoltaics and Optoelectronics ( IPEROP25), which will be held on January 21 and 22, 2025, at Kyoto University’s Uji Campus.
About EneCoat Technologies
EneCoat Technologies is a startup company established in January 2018,based on the research results of Atsushi Wakamiya’s laboratory at the Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University. The company’s corporate mission is to contribute to the realization of a carbon-neutral society through the development of lightweight thin-film solar cells for high-illumination (outdoor) applications.
The development of solar cells for automotive applications is part of the aforementioned (2) contribution to the realization of a carbon-neutral society through lightweight thin-film solar cells for high-illumination (outdoor) applications, and we are committed to realizing a rich automotive lifestyle and reducing CO2 emissions in the automobile sector.
Press release here
Company Name : EneCoat Technologies Co.Ltd., https://www.enecoat.com/
Location: 43-1 Sako Sotoyashiki, Kumiyama-cho, Kuse-gun, Kyoto, Japan
Representative: Naoya Kato, Representative Director, Executive Officer and CEO
Capital :JPY 90 million
Business: Development, manufacture and sales of perovskite solar cells and related materials, etc.
EneCoat Technologies Raises Series C Round, Totaling 5.5 Billion Yen Accelerating development of proprietary perovskite cell technology that can diversify solar supply chains, support IoT devices and mobility applications
Our company was featured in the Wall Street Journal.
Our company was featured in the Wall Street Journal on 11 January 2024.
China’s Solar Dominance Faces New Rival: An Ultrathin Film
Please take a look.
EneCoat Technologies Co., Ltd and Toyota Commence Joint Development of Perovskite Solar Cells for Automotive Applications ~Next-generation solar cells with high power generation efficiency and expected to reduce CO2 emissions during driving
Launching a verification operation of next generation solar cells (Perovskite Solar Cells) installed in IoT Co2 sensor terminal in Tokyo Metropolitan Government facilities.
EneCoat Technologies Co., Ltd (Head Office: Kumiyama-cho, Kuze-gun, Kyoto; President: Naoya Kato) has announced today a collaboration with Macnica, Inc. (Headquarters: Kohoku-ku, Yokohama; President: Kazumasa Hara), a total service and solution provider in semiconductors, networking, cyber security, and AI/IoT, and the Tokyo Metropolitan Government announced today that they have started verification operation of IoT CO2 sensor terminals equipped with perovskite solar cells (PSCs), which are considered a major next-generation solar cell technology, inside Tokyo Metropolitan Government facilities.
PSCs have excellent power generation performance both indoors and outdoors, and because they are thin, light, and bendable, they have a much wider range of applications compared to conventional solar cells, and can provide an independent power source anywhere as long as there is a light source, from small devices around us to in-car power sources, wall mounting, and space applications.
EneCoat has developed PSCs optimized for IoT terminals in terms of power generation capacity and shape, and has been conducting verification operation of air quality sensors employing PSCs made by EneCoat in collaboration with Macnica since last year and to further materialize the efforts, the agreement for the verification operation was signed by Macnica, the Tokyo Metropolitan Government, and EneCoat. By having the Tokyo Metropolitan Government provide offices within the Tokyo Metropolitan Government Building as an environment for air quality monitoring operation, Macnica, the Tokyo Metropolitan Government, and EneCoat will be able to further advance the study and verification of the mass production of IoT sensors equipped with PSCs.
■Roles in the Demonstration Experiment
Macnica Corporation:
Provision of sensors and systems with perovskite solar cells, installation, measurement, dissemination of the project, etc.
Tokyo Metropolitan Government:
Provision of Tokyo Metropolitan Government facilities for the verification experiment, overall coordination of the project, dissemination of the project, etc.
EneCoat Technologies Inc:
Provision of perovskite solar cells, verification of power generation performance, dissemination of the project, etc.
EneCoat is a Kyoto University startup established in 2018 to commercialize the research results of Atsushi Wakamiya’s laboratory at the Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, and has positioned as a corporate mission to contribute to (1) the promotion of IoT by devices using highly efficient solar cells for low illumination and (2) the realization of a carbon neutral society by lightweight thin film solar cells for high illumination.
Taking the opportunity of the development of the IoT CO2 sensor, EneCoat will expand its lineup of high-performance PSCs for sensors and wearable devices, aiming to start production by the end of 2024.